Lemon Tree Care & Benefits | Grow Healthy Citrus
Published: 2025-10-19
Introduction to Lemon Tree Care
Lemon trees are among the most rewarding fruit trees to grow. Not only do they produce vibrant citrus fruits but they also enhance garden aesthetics. Whether planted in the ground or grown in containers, lemon trees thrive with proper care. Because of their versatility and health benefits, they have become a favorite among home gardeners.
To grow healthy citrus, understanding the basics of lemon tree care is essential. From soil preparation to pest control, each step contributes to a thriving tree. Moreover, lemon trees can be cultivated in various climates with the right techniques. Therefore, this guide will walk you through everything needed to grow and maintain a productive lemon tree.
Choosing the Right Lemon Tree Variety
Before planting, selecting the right variety is crucial. Popular types include:
- Eureka Lemon – Common in warm climates and known for year-round fruiting
- Meyer Lemon – A hybrid with sweeter flavor and compact growth
- Lisbon Lemon – Hardy and highly productive in full sun
Each variety has unique traits. Meyer lemons, for instance, are ideal for container gardening. On the other hand, Lisbon lemons are better suited for large outdoor spaces. Because climate and space influence growth, choosing accordingly ensures success.
| Ideal Growing Conditions for Lemon Trees |
|---|
Lemon trees flourish in warm, sunny environments. They require: Although lemon trees prefer subtropical climates, they can be grown indoors or in cooler zones with proper care. For instance, container lemon trees can be moved indoors during winter. Because temperature fluctuations affect growth, consistent warmth is beneficial. |
Planting Lemon Trees Step-by-Step
To plant a lemon tree successfully:
- Choose a Sunny Spot – Ensure the location receives direct sunlight
- Prepare the Soil – Mix compost and sand for drainage
- Dig a Hole – Twice as wide as the root ball
- Place the Tree – Ensure the graft line stays above soil level
- Backfill and Water – Gently pack soil and water thoroughly
After planting, mulch should be added around the base. This helps retain moisture and suppress weeds. However, mulch must not touch the trunk to prevent rot. Because root health is vital, proper planting sets the foundation for long-term success.
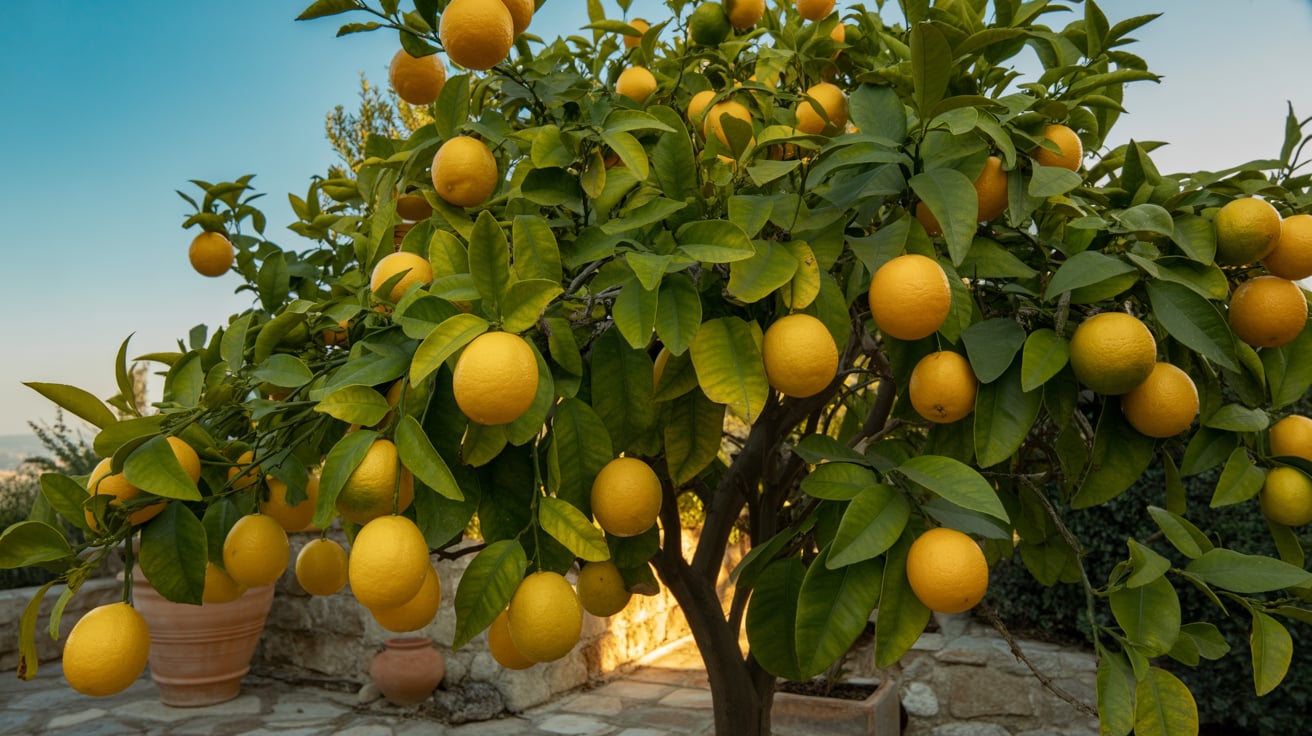

Watering and Moisture Management
Lemon trees need consistent watering, especially during dry spells. Young trees should be watered every 2 to 3 days. Mature trees require deep watering once a week. Overwatering must be avoided because it leads to root rot.
To check moisture levels:
- Insert a finger 2 inches into the soil
- If dry, water thoroughly
- If moist, wait another day
Drip irrigation systems are ideal for maintaining consistent moisture. Moreover, watering should be done early in the morning. Because evaporation rates are lower, water is absorbed more efficiently.
Fertilization plays a key role in citrus health. Lemon trees benefit from:
- Nitrogen-Rich Fertilizers – Promote leaf and branch growth
- Micronutrients – Zinc, magnesium and iron support fruit development
- Slow-Release Formulas – Ensure steady nutrient supply
Fertilizer should be applied every 4 to 6 weeks during the growing season. Organic options like compost tea and fish emulsion are also effec
Pruning Lemon Trees for Shape and Health
Pruning improves air circulation and sunlight penetration. It also helps control size and remove diseased branches. Lemon trees should be pruned:
- In Late Winter or Early Spring – Before new growth begins
- To Remove Dead or Crossing Branches – Prevents fungal infections
- To Shape the Canopy – Encourages balanced growth
Sterilized pruning shears must be used to avoid spreading disease. Moreover, pruning stimulates new growth and enhances fruit production. Because crowded branches reduce airflow, strategic trimming is beneficial.
Common Lemon Tree Pests and Diseases
Lemon trees are vulnerable to several pests and diseases. Common issues include:
- Aphids – Cause leaf curling and sap loss
- Scale Insects – Appear as bumps on stems and leaves
- Leaf Miners – Tunnel through leaves causing damage
- Citrus Canker – Bacterial infection leading to lesions

To manage pests organically:
- Spray neem oil or insecticidal soap
- Introduce beneficial insects like ladybugs
- Remove infected leaves promptly
Disease prevention involves proper spacing and sanitation. Because pests weaken trees and reduce yield, early intervention is key.
Growing Lemon Trees in Containers
Container gardening offers flexibility for lemon tree enthusiasts. It allows cultivation in small spaces and colder climates. Because containers can be moved indoors, they protect trees from frost and harsh weather.
To grow lemon trees in pots:
- Choose a Large Container – Minimum 5 gallons with drainage holes
- Use Citrus Potting Mix – Ensures proper aeration and pH balance
- Place in Full Sun – South-facing windows or patios work best
Container lemon trees require more frequent watering and feeding. Because nutrients leach out faster, monthly fertilization is recommended. Moreover, root pruning every 2 to 3 years keeps the tree healthy and compact.
Seasonal Lemon Tree Care Tips
Lemon trees respond differently to seasonal changes. Adjusting care throughout the year ensures consistent growth and fruiting.
Spring
- Apply fertilizer to boost new growth
- Prune lightly to shape the canopy
- Watch for aphids and scale insects
Summer
- Increase watering during hot spells
- Protect from sunburn with shade cloth if needed
- Harvest ripe lemons regularly
Fall
- Reduce watering as temperatures drop
- Apply potassium-rich fertilizer to strengthen roots
- Inspect for fungal infections

Winter
- Move container trees indoors or cover outdoor trees
- Avoid overwatering due to slow growth
- Maintain humidity with trays or misting
Because seasonal care prevents stress and disease, adapting your routine is essential.
| Health Benefits of Lemons |
|---|
Lemons are packed with nutrients and antioxidants. Their health benefits include:
Fresh lemon juice can be added to water, tea or recipes. Because le |
Lemon Tree Flowering and Fruiting Cycle
Understanding the flowering cycle helps maximize yield. Lemon trees typically bloom in spring and summer. Flowers appear in clusters and emit a sweet fragrance. Pollination is required for fruit set.
To encourage flowering:
- Ensure adequate sunlight and nutrients
- Avoid excessive nitrogen during bloom
- Hand-pollinate indoor trees using a soft brush
Fruit development takes 4 to 6 months. Lemons turn from green to yellow as they ripen. Because consistent care influences fruit quality, monitoring the cycle is important.
Soil Testing and pH Management
Soil health directly affects lemon tree performance. Testing soil annually helps maintain optimal conditions. Ideal pH ranges from 5.5 to 6.5.
To adjust pH:
- Add sulfur to lower pH
- Use lime to raise pH
- Apply compost for balanced nutrients
Soil test kits are available at garden centers. Because nutrient uptake depends on pH, regular monitoring is recommended.

Organic Pest Control Methods
Organic gardening promotes sustainability and safety. Lemon trees can be protected using natural methods.
Effective strategies include:
- Neem Oil Sprays – Disrupt pest life cycles
- Companion Planting – Basil and marigold repel insects
- Sticky Traps – Capture flying pests
- Beneficial Insects – Ladybugs and lacewings eat aphids
Avoid chemical pesticides that harm pollinators. Because organic methods preserve ecosystem balance, they are preferred by eco-conscious gardeners.
Mulching and Weed Prevention
Mulching conserves moisture and suppresses weeds. Organic mulches like straw, bark or compost work best. Apply a 2 to 3-inch layer around the base.
Benefits of mulching:
- Reduces evaporation
- Prevents weed competition
- Regulates soil temperature
- Adds nutrients as it decomposes
Keep mulch 2 inches away from the trunk. Because excessive moisture near the trunk causes rot, spacing is important.
Diagnosing Nutrient Deficiencies
Lemon trees show visible signs when nutrients are lacking. Common symptoms include:
- Yellow Leaves – Nitrogen or iron deficiency
- Leaf Curling – Potassium imbalance
- Poor Fruit Set – Lack of phosphorus
To correct deficiencies:
- Use citrus-specific fertilizers
- Apply foliar sprays for quick absorption
- Amend soil with compost or organic matter
Because early diagnosis prevents long-term damage, regular inspection is advised.

Propagating Lemon Trees from Cuttings
Propagation allows gardeners to clone healthy lemon trees. It’s cost-effective and ensures genetic consistency. Because seeds may not produce true-to-type fruit, cuttings are preferred.
To propagate lemon trees:
- Select Healthy Branches – Choose semi-hardwood stems 6 to 8 inches long
- Remove Lower Leaves – Leave only the top two
- Dip in Rooting Hormone – Encourages root development
- Plant in Moist Potting Mix – Use a container with drainage
- Cover with Plastic Dome – Retains humidity
Roots form in 4 to 6 weeks. Once established, transplant into larger pots or garden beds. Because propagation requires patience, consistent care is essential.
Advanced Pruning Techniques for Citrus Trees
Beyond basic pruning, advanced methods improve productivity. These include:
- Thinning Cuts – Remove entire branches to open the canopy
- Heading Cuts – Trim tips to encourage bushier growth
- Skirt Pruning – Remove lower branches to prevent soil contact
Pruning should be done with sterilized tools. Avoid pruning during frost or extreme heat. Because timing affects recovery, late winter is ideal.
Troubleshooting Common Lemon Tree Problems
Even with proper care, lemon trees may face challenges. Identifying issues early prevents long-term damage.
Problem: Yellow Leaves
- Cause – Nitrogen deficiency or poor drainage
- Solution – Apply balanced fertilizer and improve soil aeration
Problem: Leaf Drop
- Cause – Overwatering or sudden temperature changes
- Solution – Adjust watering schedule and protect from drafts
Problem: No Flowers or Fruit
- Cause – Excess nitrogen or lack of sunlight
- Solution – Switch to phosphorus-rich fertilizer and ensure full sun exposure
Because symptoms often overlap, careful observation is necessary.

Encouraging Seasonal Fruiting
Lemon trees can fruit multiple times a year. However, peak production occurs in spring and summer. To boost fruiting:
- Maintain Consistent Watering – Stress reduces flower formation
- Use Bloom-Boosting Fertilizers – High in phosphorus and potassium
- Hand-Pollinate Indoor Trees – Improves fruit set
Avoid pruning during bloom. Because flowers develop into fruit, preserving them is crucial.
Cleaning and Sanitizing Tools
Clean tools prevent disease spread. After each use:
- Wipe blades with alcohol or bleach solution
- Dry thoroughly to prevent rust
- Store in a dry place
Because citrus diseases spread easily, sanitation is non-negotiable.
Frost Protection for Lemon Trees
Cold damage can kill lemon trees. To protect them:
- Use Frost Blankets – Cover trees during cold nights
- Add Mulch – Insulates roots
- Move Containers Indoors – Keep near sunny windows
Avoid watering during freezing conditions. Because ice expands in soil, root damage may occur.
Monitoring Citrus Tree Growth
Tracking growth helps optimize care. Key indicators include:
- Leaf Color – Healthy trees have deep green leaves
- Branch Density – Balanced canopy allows airflow
- Fruit Size and Quantity – Indicates nutrient availability
Use garden journals or apps to log progress. Because data reveals patterns, adjustments become easier.
Composting for Citrus Trees
Compost enriches soil and improves structure. Ideal compost includes:
- Fruit peels
- Coffee grounds
- Grass clippings
- Dry leaves
Apply compost around the base monthly. Because organic matter improves drainage and fertility, it supports healthy growth.
Harvesting Lemons at Peak Ripeness
Knowing when to harvest lemons ensures the best flavor and nutrition. Lemons are ready when:
- Skin turns bright yellow
- Fruit feels firm but slightly soft
- Size reaches 2 to 3 inches in diameter
To harvest:
- Use pruning shears or twist gently
- Avoid pulling to prevent branch damage
- Harvest regularly to encourage new blooms
Because lemons do not ripen after picking, timing is crucial. Frequent harvesting also reduces pest attraction.

Storing and Preserving Lemons
Proper storage extends shelf life and maintains freshness. Fresh lemons can be stored:
- At Room Temperature – For up to 1 week
- In the Refrigerator – Lasts 3 to 4 weeks
- In Airtight Containers – Prevents moisture loss
Preservation methods include:
- Freezing lemon juice in ice trays
- Drying lemon zest for seasoning
- Making lemon preserves or marmalade
Because lemons are versatile, preserving them reduces waste and enhances culinary options.
Culinary Uses of Lemons
Lemons add brightness and acidity to dishes. Popular uses include:
- Salad Dressings – Combine with olive oil and herbs
- Marinades – Tenderize meats and fish
- Baking – Lemon zest enhances cakes and cookies
- Beverages – Lemon water and lemonade refresh and hydrate
Lemon peels can be candied or infused into oils. Because of their intense flavor, small amounts go a long way.
Companion Planting with Lemon Trees
Companion planting improves pest control and soil health. Ideal companions include:
- Basil – Repels aphids and enhances flavor
- Marigold – Deters nematodes and whiteflies
- Lavender – Attracts pollinators and repels moths
- Garlic – Prevents fungal infections
Avoid planting near tall trees that block sunlight. Because lemon trees need space and light, strategic placement matters.
Sustainable Citrus Gardening Practices
Eco-friendly gardening supports long-term health. Sustainable practices include:
- Rainwater Harvesting – Reduces water waste
- Composting – Recycles kitchen and garden waste
- Organic Fertilizers – Avoids chemical runoff
- Integrated Pest Management – Combines natural and mechanical controls
Use biodegradable pots and avoid plastic mulch. Because sustainability benefits both plants and the planet, it’s worth the effort.
Monitoring Lemon Tree Health with Technology
Modern tools simplify garden management. Useful tech includes:
- Soil Moisture Sensors – Prevent overwatering
- Weather Apps – Track frost and rainfall
- Plant Health Trackers – Log growth and symptoms
Smart irrigation systems adjust watering automatically. Because technology enhances precision, it supports healthier trees.
Safety Tips for Citrus Gardening
Gardening should be safe and enjoyable. Follow these tips:
- Wear gloves when pruning or handling fertilizer
- Use eye protection when spraying organic solutions
- Keep tools sharp and clean to avoid injury
- Store chemicals and tools away from children
Because safety prevents accidents, it should never be overlooked.
Lemon Tree Growth Timeline
Understanding growth stages helps set expectations:
- Year 1 – Establishes roots and foliage
- Year 2 – Begins flowering and limited fruiting
- Year 3+ – Full fruit production and canopy development
Growth may vary based on climate and care. Because patience pays off, consistent attention is key.
Final Tips for Thriving Lemon Trees
To ensure long-term success, keep these tips in mind:
- Monitor Soil Moisture Weekly – Prevents overwatering and root rot
- Use Citrus-Specific Fertilizers – Supports balanced growth and fruiting
- Prune Annually – Improves airflow and shape
- Protect from Frost – Use covers or move containers indoors
- Inspect for Pests Monthly – Early detection prevents damage
Because consistency matters, create a seasonal care calendar. This helps track tasks and anticipate challenges.

Recap: Why Grow Lemon Trees?
Lemon trees offer beauty, nutrition and sustainability. They:
- Produce vitamin-rich fruit year-round
- Enhance garden aesthetics with fragrant blooms
- Support eco-friendly gardening practices
- Thrive in containers or outdoor spaces
- Provide culinary and medicinal benefits
Whether you’re a beginner or seasoned gardener, lemon trees reward your efforts. Because they adapt to various climates and spaces, they’re ideal for home cultivation.
FAQs
Young trees need water every 2–3 days. Mature trees require deep watering once a week. Always check soil moisture before watering.
Use citrus-specific fertilizers rich in nitrogen, magnesium and potassium. Apply every 4–6 weeks during the growing season.
Yes. Choose dwarf varieties like Meyer lemon. Place near a sunny window and use containers with good drainage.
Common causes include nitrogen deficiency, overwatering or poor drainage. Adjust fertilizer and check soil conditions.
Most lemon trees bloom in spring and summer. Fruit ripens in 4–6 months. Some varieties produce year-round.
Q6: How do I protect my lemon tree from frost?
A: Use frost blankets, mulch around the base and move containers indoors. Avoid watering during freezing temperatures.
Q7: What pests affect lemon trees?
A: Aphids, scale insects and leaf miners are common. Use neem oil, sticky traps or introduce beneficial insects.
Q8: Can I grow lemon trees from seeds?
A: Yes, but seed-grown trees may not produce true-to-type fruit. Cuttings or grafted trees are more reliable.
Q9: How do I prune my lemon tree?
A: Prune in late winter. Remove dead or crossing branches and shape the canopy. Use sterilized tools.
Q10: What are the health benefits of lemons?
A: Lemons boost immunity, aid digestion, support weight loss and improve skin health. They’re rich in vitamin C and antioxidants.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks



- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks