Container Gardening: Grow Fresh Veggies Without a Backyard
Published: 2025-10-18
Introduction: Why Container Gardening Works Anywhere
Container gardening has become a top choice for urban dwellers. It allows fresh vegetables to be grown without a backyard. Plant pots, grow bags and vertical planters can be used on balconies and rooftops. Organic compost and proper drainage ensure healthy growth. This guide will help you grow vegetables in containers from seed to harvest.
Step 1: Choosing the Right Containers
Containers must be selected based on plant type. Tomatoes and peppers need deep pots. Leafy greens grow well in shallow containers. Drainage holes should be present to avoid root rot. Grow bags and recycled buckets can also be used.
Plastic, clay and ceramic pots are commonly available. Lightweight containers are easier to move. Raised plant stands improve air circulation. Organic compost should be added before planting.
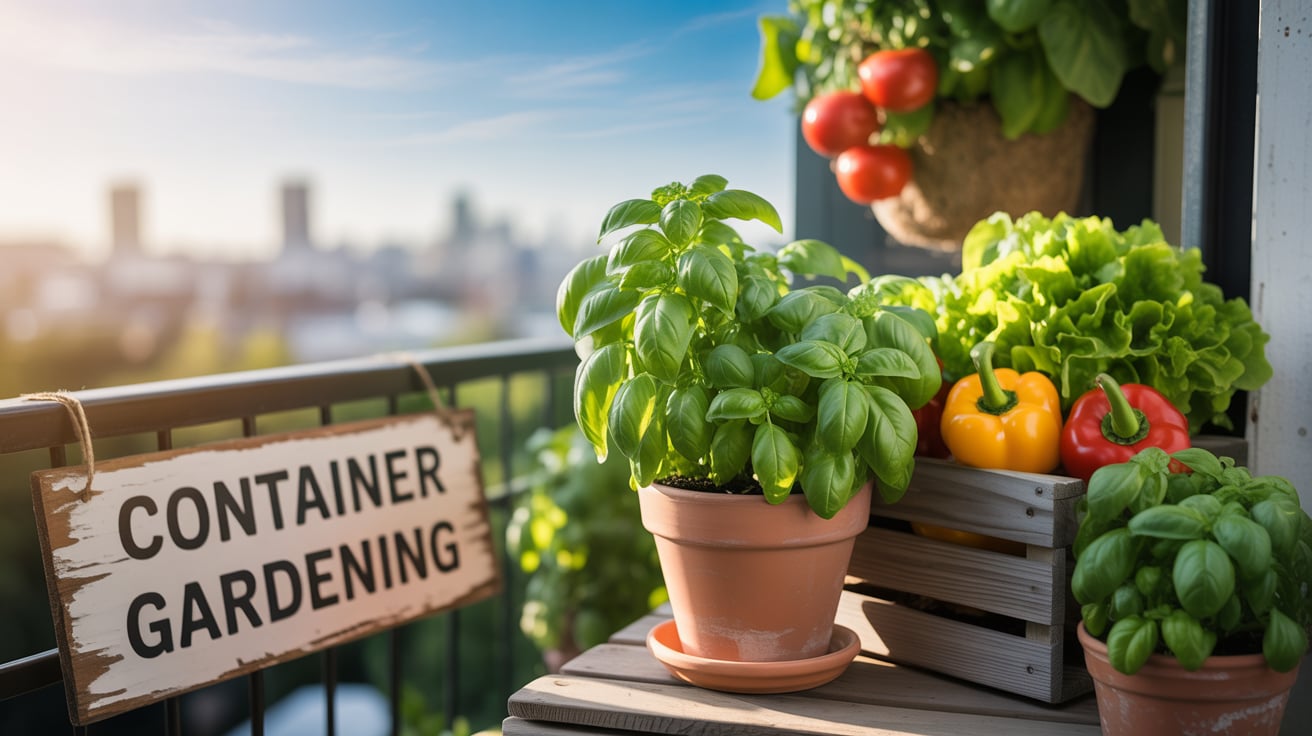

Step 2: Selecting the Best Soil Mix
Soil quality affects vegetable yield. A mix of potting soil and organic compost should be used. Perlite and coco coir improve aeration. Fertilizer must be added every few weeks. Moisture retention is essential for container gardening.
Soil should be loose and well-draining. Heavy garden soil must be avoided. Organic compost improves nutrient levels. Mulch can be added to reduce evaporation.
Step 3: Picking the Right Vegetables
Vegetables must be chosen based on space and sunlight. Tomatoes, peppers and beans grow well in containers. Leafy greens like spinach and lettuce require less space. Root vegetables like carrots and radishes need deeper pots.
Seed packets provide planting depth and spacing instructions. Organic seeds are preferred for chemical-free produce. Seasonal planting ensures continuous harvest. Companion planting helps deter pests naturally.
Step 4: Planting Seeds or Seedlings
Seeds should be planted according to packet instructions. Depth and spacing must be followed. Seedlings can be transplanted once roots are established. Containers should be placed in sunny spots.
Watering must be done gently to avoid displacement. Organic compost should be mixed into the soil. Mulch can be added to retain moisture. Labels should be used to track plant types.
Step 5: Watering and Fertilizing
Watering should be consistent. Overwatering must be avoided. Containers dry out faster than garden beds. Early morning is the best time to water. Fertilizer should be added every two weeks.
Compost tea can be used as a natural fertilizer. Liquid feeds are absorbed quickly. Soil moisture must be checked regularly. Mulch helps retain water and reduce weeds.
Step 6: Managing Pests and Diseases
Pests must be monitored regularly. Neem oil can be sprayed to deter insects. Fungal infections can be prevented with proper spacing. Organic gardening reduces chemical use.
Companion planting helps protect crops. For example, basil repels aphids when planted near tomatoes. Containers should be cleaned between seasons. Mulch can be used to suppress weeds.
Step 7: Supporting Plant Growth
Stakes and cages should be used for tall plants. Tomatoes and beans benefit from vertical support. Hanging baskets and trellises save space. Containers can be moved to sunnier spots if needed.
Pruning must be done to encourage growth. Dead leaves should be removed. Organic compost boosts plant health. Labels help track growth stages.
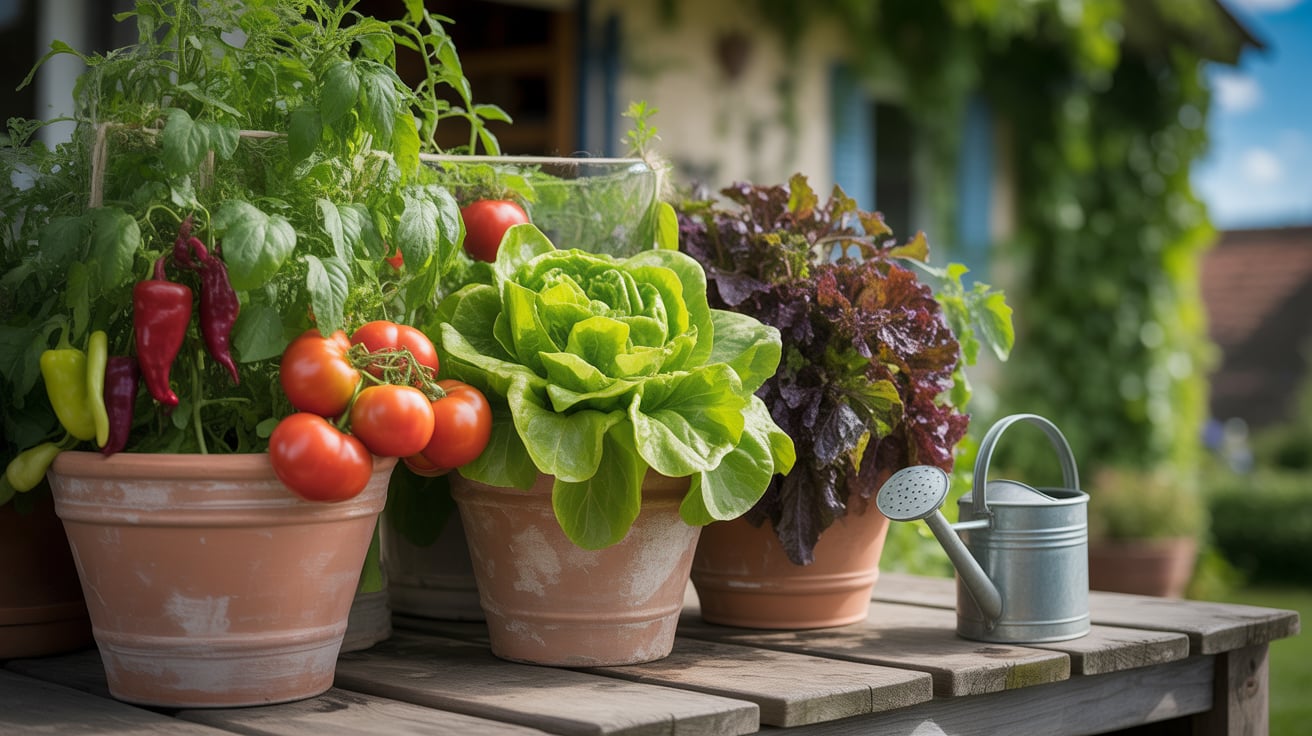

Step 8: Harvesting Your Vegetables
Harvesting should be done when vegetables reach maturity. Leafy greens can be picked early. Root vegetables must be pulled gently. Tomatoes should be harvested when fully colored.
Containers make harvesting easier. Compost can be added post-harvest. Seeds should be saved for the next season. Labels help track harvest dates.
Step 9: Storing and Using Your Produce
Vegetables should be washed and dried. Refrigeration helps extend shelf life. Composting leftovers reduces waste. Containers can be reused for herbs.
Organic gardening supports healthy eating. Fresh produce can be used in daily meals. Herbs add flavor and nutrition. Seeds should be stored in a cool dry place.
Step 10: Preparing for the Next Season
Soil should be tested again. Compost must be replenished. Containers should be cleaned and stored. Seeds should be organized by type.
Seasonal planting ensures continuous harvest. Organic gardening improves soil health. Labels help track planting cycles. Mulch should be added before planting.
Bonus Tips for Container Gardening Success
- Use compost regularly
- Rotate crops each season
- Choose disease-resistant seeds
- Water early in the morning
- Keep a gardening journal
Why Container Gardening Is the Future of Urban Food
Container gardening has become one of the most popular methods for growing vegetables in urban areas. With limited space and increasing food costs, people are turning to plant pots and balcony gardens to grow their own produce. This method allows fresh vegetables to be grown without a backyard. It is ideal for apartments, rooftops and small patios. Organic compost and proper drainage make it possible to grow healthy crops in containers.
Unlike traditional gardening, container gardening requires less space and fewer tools. It can be started with minimal investment. Plant pots can be reused and moved easily. Raised plant stands improve air circulation and sunlight exposure. Urban gardening has gained momentum due to its flexibility and sustainability. Vegetables like tomatoes, spinach and peppers thrive in containers. Herbs such as basil and mint grow well in small pots.

Choosing the Right Containers for Your Garden
Containers must be selected based on the type of vegetable being grown. Tomatoes and peppers require deep pots while leafy greens grow well in shallow containers. Drainage holes should be present to prevent root rot. Grow bags and recycled buckets can also be used. These options are affordable and eco-friendly.
Plastic, clay and ceramic pots are commonly available. Each material has its own benefits. Plastic pots are lightweight and easy to move. Clay pots provide better insulation but may crack in cold weather. Ceramic pots are decorative and durable. Raised plant stands help improve airflow and reduce pests.
Container size affects root development. Larger pots allow more room for growth. Small containers are suitable for herbs and microgreens. Hanging baskets can be used for trailing plants like strawberries. Vertical planters save space and add visual appeal.
Selecting the Best Soil Mix for Container Gardening
Soil quality plays a crucial role in container gardening. A mix of potting soil and organic compost should be used. Perlite and coco coir improve aeration and moisture retention. Fertilizer must be added every few weeks to maintain nutrient levels. Mulch can be used to reduce evaporation and suppress weeds.
Heavy garden soil should be avoided. It compacts easily and restricts root growth. Potting soil is designed for containers and provides better drainage. Organic compost enriches the soil and supports microbial activity. Vermicompost can be added for extra nutrients.
Soil pH should be tested before planting. Most vegetables prefer a pH between 6.0 and 7.0. Lime or sulfur can be added to adjust pH levels. Soil should be loose and crumbly. Moisture levels must be checked regularly.
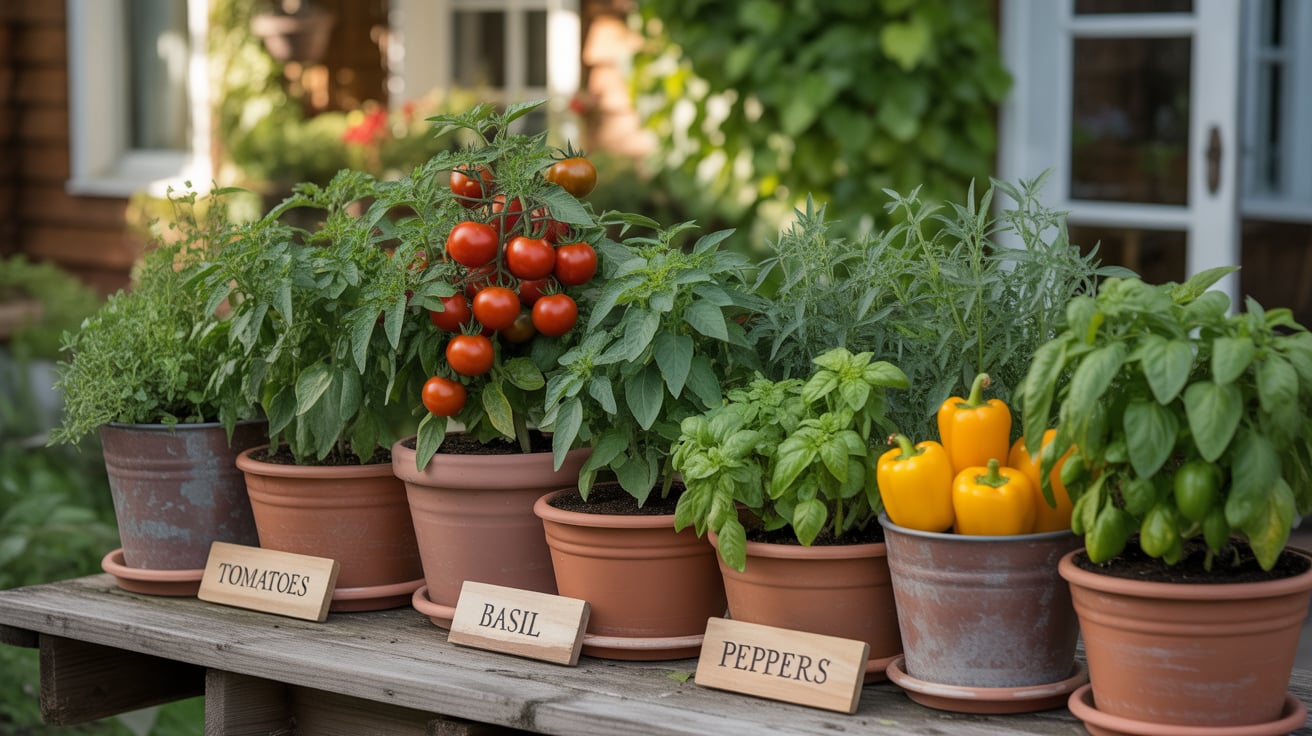

Picking the Right Vegetables for Containers
Vegetables must be chosen based on space and sunlight availability. Tomatoes, peppers and beans grow well in containers. Leafy greens like spinach and lettuce require less space. Root vegetables such as carrots and radishes need deeper pots.
Seed packets provide planting depth and spacing instructions. Organic seeds are preferred for chemical-free produce. Seasonal planting ensures continuous harvest. Companion planting helps deter pests naturally. For example, basil repels aphids when planted near tomatoes.
Some vegetables grow better in cooler climates. Others prefer warm temperatures. Spinach and peas thrive in spring while cucumbers and eggplants do well in summer. Fall is suitable for second rounds of carrots and kale. Containers allow flexibility in planting schedules.
Tomatoes, peppers and leafy greens grow well.
Every 4 to 6 weeks.
Yes, with proper sunlight and containers.
Early morning
Use neem oil and companion planting.
Yes, after cleaning and adding fresh soil.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks



- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks